Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yano, Yasuhide; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanno, Takashi; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of fast neutron irradiation on tensile properties of modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) claddings and wrappers for fast reactors were investigated. PNC316 claddings and wrappers were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo at irradiation temperatures between 400 and 735  C to fast neutron doses ranging from 21 to 125 dpa. The post-irradiation tensile tests were carried out at room and irradiation temperatures. Elongations of PNC316 measured by the tensile tests were maintained at an engineering level, although the material incurred significant irradiation hardening and softening. The maximum swelling of PNC316 wrappers was about 2.5 vol.% at irradiation temperature between 400 and 500
C to fast neutron doses ranging from 21 to 125 dpa. The post-irradiation tensile tests were carried out at room and irradiation temperatures. Elongations of PNC316 measured by the tensile tests were maintained at an engineering level, although the material incurred significant irradiation hardening and softening. The maximum swelling of PNC316 wrappers was about 2.5 vol.% at irradiation temperature between 400 and 500 C up to 110 dpa. Japanese 20% cold-worked austenitic steels, PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni, had sufficient ductility and work-hardenability even after above 10 vol.% swelling, while they had very weak plastic instabilities.
C up to 110 dpa. Japanese 20% cold-worked austenitic steels, PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni, had sufficient ductility and work-hardenability even after above 10 vol.% swelling, while they had very weak plastic instabilities.
Asayama, Tai; Otsuka, Satoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 15 Pages, 2017/06
This paper summarizes ongoing efforts in Japan Atomic Energy Agency on the development of core and structural materials for sodium-cooled fast reactors. For core materials, oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steels and 11Cr ferritic steel (PNC-FMS) will be used for the fuel pin cladding and wrapper tube, respectively. As for ODS steel, 9Cr- and 11Cr-ODS steels have been extensively developed. Their laboratory-scale manufacturing technology has been developed including reliability improvement in tube microstructure and strength homogeneity. As for the PNC-FMS wrapper tube, the development of a dissimilar joining technique with type 316 steel and properties evaluation of dissimilar welds have been carried out. For structural materials, codification of 316FR stainless steel and Modified 9Cr-1Mo steel is ongoing. Acquisition and collection of long-term data of base metal and welded joints are continued and evaluation methodologies are being developed to establish a technical basis for 60-year design.
; ; Sakamoto, Naoki; *; Akasaka, Naoaki;
JNC TN9400 2000-095, 110 Pages, 2000/07
The effects of high fluence irradiation and swelling on the transient burst properties of austenitic steel fuel claddings; PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni stcel, which were irradiated as the MONJU type fuel assemblies (MFA-1&MFA-2) in the FFTF reactor, were investigated. The temperature-transient-to-burst tests were conducted on a total of eight irradiation conditions. Fractographic examination and TEM observation were performed in order to evaluate the effect of high dose irradiation on the transient burst property and the relation between failure mechanism and microstructural change during rapid (ramp) heating. The results of the PIE showed that there was no significant effect of irradiation on the transient burst properties of these fuel claddings under the irradiation conditions examined. the results obtained in this study are as follows; (1)The rupture temperature of the irradiated PNC316 fuel cladding of MFA-1 was as same as that of our previous works for the fluence range up to 2.13 10
10 n/m
n/m . There was no noticeable decrease in rupture temperature with increasing fluence in lower hoop stress region(
. There was no noticeable decrease in rupture temperature with increasing fluence in lower hoop stress region( 100MPa). (2)The rupture temperature of the irradiated 15Cr-20Ni fuel cladding of MFA-2 was almost as same as that of as-received cladding for the hoop stress range up to about 200MPa. The rupture temperature did not decrease significantly with fluence. (3)The rupture temperature of the irradiated PNC316 cladding tested at hoop stress 69MPa, which was the design hoop stress for MONJU fuel, was 1055.6
100MPa). (2)The rupture temperature of the irradiated 15Cr-20Ni fuel cladding of MFA-2 was almost as same as that of as-received cladding for the hoop stress range up to about 200MPa. The rupture temperature did not decrease significantly with fluence. (3)The rupture temperature of the irradiated PNC316 cladding tested at hoop stress 69MPa, which was the design hoop stress for MONJU fuel, was 1055.6 C. This suggested that the design cladding maximum temperature limit for MONJU (830
C. This suggested that the design cladding maximum temperature limit for MONJU (830 C) was conservative. (4)There was no obvious relation between rupture temperature, swelling and microstructural change during transient heating under the irradiation conditions examined.
C) was conservative. (4)There was no obvious relation between rupture temperature, swelling and microstructural change during transient heating under the irradiation conditions examined.
Fujiwara, Masayuki; Mizuta, Shunji;
JNC TN9400 2000-050, 19 Pages, 2000/04
For evaluating the fast reactor system technology, it is important to evaluate the practical feasibility of ODS ferritic cdaddings, which is the most promising matelials to attain the goal of high coolant temperature and more than 150 GWd/t. Based on the results of their technology development, mass production process with highly economically benefit as well as manufacturing cost estimation of ODS ferritic claddings were preliminarily conducted. From the view point of future utility scale, the cost for manufacturig mother tubes has a dominant factor in the total manufacturing cost. The method to reduce the cost of mother tube manufacturing was also preliminarily investigated.
;
JNC TN9400 2000-035, 164 Pages, 2000/03
High Strength Ferritic/Martensitic Steel (PNC-FMS : 0.12C-11Cr-0,5Mo-2W-0.2V-0.05Nb), developed by JNC, is one of the candidate materials for the long-life core of large-scale fast breeder reactor. Ductile brittle transition temperature (DBTT) was tentatively determined in 1992 in material design base standard of PNC-FMS. Howevcr, specimen size effect on impact property and upper shelf energy (USE) have not been evaluated. ln this study, effects of specimen size, thermal aging and neutron irradiation on the charpy impact property of PNC-FMS were evaluated, using together with recently obtained data. The design value of USE and DBTT as fabricated and each correlation of aging and irradiation effects were determined. The results are summarized as follows. (1)lt was found that USE is related to (Bb) as USE=m(Bb)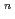 , where B is specimen width, b is ligament size and both m and n are constant. For PNC-FMS, n value is equal to 1.4. It's possible to determine n value from USE (J) for full size specimen using the correlation: n=1.38
, where B is specimen width, b is ligament size and both m and n are constant. For PNC-FMS, n value is equal to 1.4. It's possible to determine n value from USE (J) for full size specimen using the correlation: n=1.38 10
10 USE + 1.20. (2)lt was clarified that DBTT is correlated with (BKt) as DBTT=p(log
USE + 1.20. (2)lt was clarified that DBTT is correlated with (BKt) as DBTT=p(log BKt)+q, where Kt is elastic stress concentration factor and both p and q are constant. For PNC-FMS, the correlation is as follows: DBTT=119(log
BKt)+q, where Kt is elastic stress concentration factor and both p and q are constant. For PNC-FMS, the correlation is as follows: DBTT=119(log BKt)-160. (3)DBTT estimated at the irradiation temperature from 350 to 650
BKt)-160. (3)DBTT estimated at the irradiation temperature from 350 to 650  C for sub size specimen (width and height are 3 and 10 mm, respectively), was below 180
C for sub size specimen (width and height are 3 and 10 mm, respectively), was below 180  C, based on the design value of DBTT as fabricated and each correlation of aging and irradiation effects.
C, based on the design value of DBTT as fabricated and each correlation of aging and irradiation effects.
; Yamagata, Ichiro; Donomae, Takako; Akasaka, Naoaki
JNC TN9400 2000-046, 24 Pages, 2000/02
lt is well known that solute atoms are segregated on surface, grain boundary, etc. and composition changed partially in irradiated austenitic stainless steel. For understanding radiation induced segregation (RIS), we adopt a Fe-15Cr-20Ni-x (x: Si, Mo) which is basically alloy system in PNC1520, and size of Si, Mo are different from matrix atoms to investigate RIS behaviors. The specimens were irradiated by "Joyo" fast reactor that irradiation condition is 3.5  10
10 n/m
n/m (E>0.1Mev) at 476
(E>0.1Mev) at 476 C. After irradiation, the specimen were observed and analyzed with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope) of 400kV TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The behavior of RIS depends on size of solute atoms of alloy. For example, oversized atoms are decreased and undersized atoms are increased in sink. RIS of voids are as same as or more than grain boundaries and smaller than precipitates. The void denuded zone was existed nearby G.B. in case of combinations between the grains from G.B.0ne of the reasons in this, the voids swepted by moving G.B. in radiation induced G.B. migration.
C. After irradiation, the specimen were observed and analyzed with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope) of 400kV TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The behavior of RIS depends on size of solute atoms of alloy. For example, oversized atoms are decreased and undersized atoms are increased in sink. RIS of voids are as same as or more than grain boundaries and smaller than precipitates. The void denuded zone was existed nearby G.B. in case of combinations between the grains from G.B.0ne of the reasons in this, the voids swepted by moving G.B. in radiation induced G.B. migration.
Mizuta, Shunji; ;
JNC TN9400 99-082, 60 Pages, 1999/10
The density measurement of the internal creep specimens irradiated in FFTF/MOTA (Fast Flux Test Facility / Material open Test Assembly) was conducted MMF (Materia1 Monitoring Facility) and accurate separation of swelling strain from total strain leaded in the derivation of the irradiation creep coefficients. Irradiation creep coefficients for PNC 316, 15Cr-20Ni base S.S. and 14Cr-25Ni base S.S. were systematically expressed, while thermal creep coefficients K, under irradiation were separately expressed for above three steels. The results obtained are follows, (1)The effect of stress induced swelling was recognized in the temperature range from 405 to 605 C. The swelling in high stress specimens have a tendency to increasing swelling. (2)The irradiation creep coefficients derived from PNC316 and l5Cr-20Ni are similar to that of derived from 20%CW316S.S., CW316Ti and CW15-15Ti which were reported by other authors. (3)The irradiation creep coefficient derived from gas pressurized tube irradiation using FFTF/MOTA expressed appropriately irradiation creep strain from fuel pins using FFTF/MFA-2(15Cr-2ONi base S.S.).
C. The swelling in high stress specimens have a tendency to increasing swelling. (2)The irradiation creep coefficients derived from PNC316 and l5Cr-20Ni are similar to that of derived from 20%CW316S.S., CW316Ti and CW15-15Ti which were reported by other authors. (3)The irradiation creep coefficient derived from gas pressurized tube irradiation using FFTF/MOTA expressed appropriately irradiation creep strain from fuel pins using FFTF/MFA-2(15Cr-2ONi base S.S.).
Hunter
PNC TN9410 98-015, 81 Pages, 1998/02
The study was carried out within the framework of the PNC-CEA collaboration agreement. Data were provided, by CEA, for an experimental loading of a start-up core in Super-Phenix. This data was used at PNC to produce core flux snapshot calculations. CEA undertook a comparison of the PNC results with the equivalent calculations carried out by CEA, and also with experimental measurements from SPX. The resu1ts revealed a systematic radial flux tilt between the calculations and the reactor measurements, with the PNC tilts only  30-401 of those from CEA. CEA carried out an analysis of the component causes of the radial tilt. It was concluded that a major cause of radia1 tilt differences between the PNC and CEA calculations lay in the nuclear datasets used: JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV. For the final stage of the study, PNC undertook a sensitivity analysis, to examine the detailed differences between the two sets of nuclear data. The PNC flux calculations modelled SPX in both 2D (RZ) and 3D (hex-Z) geometries, using the diffusion programs CITATION and MOSES. The sensitivity analysis of the differences between the JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV nuclear datasets used the SAGEP calculational route. Both datasets were condensed to a single, non-standard, set of energy group boundaries. There were some incompatibilities in the cross-section formats of the two datasets. The sensitivity analysis showed that a relatively small number of nuclear data items contributed the bulk of the radial tilt difference between calculations with JENDL-3.2 and with CARNAVAL IV. A direct comparison between JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV data revealed the following. The Nu values showed little difference (<5|%). The only large fission cross-section differences were at low energy (<30% otherwise, with <10% typical). Although down-scattering reactions showed some large fractional differences, absolute differences were negligible compared with in-group scattering; for in-group scattering fractional ...
30-401 of those from CEA. CEA carried out an analysis of the component causes of the radial tilt. It was concluded that a major cause of radia1 tilt differences between the PNC and CEA calculations lay in the nuclear datasets used: JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV. For the final stage of the study, PNC undertook a sensitivity analysis, to examine the detailed differences between the two sets of nuclear data. The PNC flux calculations modelled SPX in both 2D (RZ) and 3D (hex-Z) geometries, using the diffusion programs CITATION and MOSES. The sensitivity analysis of the differences between the JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV nuclear datasets used the SAGEP calculational route. Both datasets were condensed to a single, non-standard, set of energy group boundaries. There were some incompatibilities in the cross-section formats of the two datasets. The sensitivity analysis showed that a relatively small number of nuclear data items contributed the bulk of the radial tilt difference between calculations with JENDL-3.2 and with CARNAVAL IV. A direct comparison between JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV data revealed the following. The Nu values showed little difference (<5|%). The only large fission cross-section differences were at low energy (<30% otherwise, with <10% typical). Although down-scattering reactions showed some large fractional differences, absolute differences were negligible compared with in-group scattering; for in-group scattering fractional ...
Ikawa, Koji; Ihara, Hitoshi; Nishimura, Hideo
JAERI-M 93-182, 160 Pages, 1993/09
no abstracts in English
Kurosawa, A.; Abe, Katsuo; Kaminaga, Kazuhiro; Kuno, Yusuke; ;
PNC TN8410 93-031, 191 Pages, 1993/03
So far, samples have been taken by both Japan Government and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) from the feed accounting tank of the Reprocessing Plant. Upon transporting the samples, one A-type transport container per batch sample has been required. To simplify the transport of samples, the resin bead technique requiring the trace amounts of samples (several mg for uranium and for plutonium) has been developed with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA being the center. This technique was introduced into the Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation (PNC) as part of the TASTEX project, and then has been incorporated into the JASPAS project as one of the joint researches between the PNC and the IAEA, in which the PNC has played a leading role. Up to now, joint experiments have been performed seven times, and the resin bead technique may have reached a certain technical level with a few technical problems. In these joint experiments, the PNC prepared and transported samples, whereas the IAEA analysed them. In addition, the PNC has investigated the resin bead technique independently. As mentioned above, the most outstanding merit of the resin bead technique lies in the simplified transport of samples. The technique is also provided with another merit by which uranium and plutonium can be measured without separating them from each other, leading to the necessity of research and development of it on the part of the Reprocessing Plant. This paper describes the results of investigation on the measurement technique of uranium and plutonium by means of the resin bead technique, together with the results from the 3rd to 7th PNC-IAEA joint experiments.
Ashida, Takashi; Sonobe, Hitoshi; Yamada, Kazuo
PNC TN8600 91-003, 38 Pages, 1991/06
no abstracts in English
Yusa, Yasuhisa; Kamei, Gento; Arai, Takashi
PNC TN8410 91-007, 18 Pages, 1990/12
This paper contains an overview of analogue studies for the assessment of long-term durability of engineered barrier materials at PNC Tokai. Materials of young age and with simple history are the most suitable for study as: (1)properties of the materials tend to deteriorate over longer historical time intervals; and (2) detailed quantitative data on time intervals and environmental conditions are more likely to be available. The following materials and their alteration phenomena were selected: (1)weathering alteration of basaltic glass (as vitrified waste form), (2)corrosion of iron in soil (as overpack), (3)illitization of smectite associated with contact metamorphism (as buffer material), (4)alteration of cement (as buffer or backfill material). (1)Weathering alteration of basaltic glass: Basaltic g1asses, from the Fuji and the Izu-Ohshima pyroclastic fall deposits were studied. The observations were made: (a)Climatological conditions have not varied significantly during the last three thousand years. Therefore, values for temperature, amount, and chemistry of ground water are quantified. (b)The cases studied could be regarded as leaching experiments in groundwater, using mass balances in water-g1ass interaction. (c)Although the groundwater is of Ca(Mg)-HCO type in the Fuji area and of Na-Cl type in the Izu-Ohshima, similar alteration ratios (2
type in the Fuji area and of Na-Cl type in the Izu-Ohshima, similar alteration ratios (2 3
3 m/1000yr) were obtained. (2)Corrosion of iron in soil: Industrial materials, such as gas/water service pipes of carbon steel or cast iron embedded in soil for 20
m/1000yr) were obtained. (2)Corrosion of iron in soil: Industrial materials, such as gas/water service pipes of carbon steel or cast iron embedded in soil for 20  110 years, were selected for an analogue study of corrosion of iron in bentonite. The maximum corrosion rates obtained so far fall in the range of 0.04
110 years, were selected for an analogue study of corrosion of iron in bentonite. The maximum corrosion rates obtained so far fall in the range of 0.04 0.09 mm/yr. (3)Illitization of smectite associated with contact metamorphism: In the Murakami bentonite deposit in central Japan, lateral variation of smectite to smectite/illite mixed-layer minerals are found in the aureole of the rhyolite intrusion body. Conversion of smectite to the
0.09 mm/yr. (3)Illitization of smectite associated with contact metamorphism: In the Murakami bentonite deposit in central Japan, lateral variation of smectite to smectite/illite mixed-layer minerals are found in the aureole of the rhyolite intrusion body. Conversion of smectite to the
; ; ; ; *; *; *; *; *; *; et al.
JAERI-M 83-158, 263 Pages, 1983/09
no abstracts in English
Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Oka, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Tachi, Yoshiaki
no journal, ,
Ferritic/martensitic (F/M) steels are candidate for core material of fast reactors (FR) because of its superior swelling resistance. A 11Cr F/M steel (PNC-FMS) have been developed for wrapper tube and cladding tube of demonstration FR in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. For demonstration of in-reactor performance and preparation of material strength standard, it is important to extend database on irradiation and thermal aging effects. In this work, ring tensile tests and hardness tests of PNC-FMS irradiated in Joyo up to 32.5 dpa at 455-835  C were carried out, and the results were compared with those of aging tests in order to clarify the irradiation effects exclusive of thermal aging effects. The UTS at RT of PNC-FMS irradiated at over 600
C were carried out, and the results were compared with those of aging tests in order to clarify the irradiation effects exclusive of thermal aging effects. The UTS at RT of PNC-FMS irradiated at over 600  C tended to be lower than those of as-received and/or thermal aged ones. The hardness showed the same trend. But, the UTS and hardness test results showed that PNC-FMS irradiated at 835
C tended to be lower than those of as-received and/or thermal aged ones. The hardness showed the same trend. But, the UTS and hardness test results showed that PNC-FMS irradiated at 835  C could be harder than that of aged one.
C could be harder than that of aged one.
Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Oka, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Tachi, Yoshiaki
no journal, ,
Ferritic/martensitic (F/M) steels are candidate for core material of fast reactors (FR) because of its superior swelling resistance. A 11Cr F/M steel (PNC-FMS) have been developed for wrapper tube and cladding tube for FR in JAEA. For demonstration of in-reactor performance and preparation of material strength standard, it is important to extend database on irradiation and thermal aging effects. In this work, ring tensile tests and hardness tests of PNC-FMS irradiated in Joyo up to 32.5 dpa at 455-835  C were carried out, and the results were compared with those of aging tests to clarify the irradiation effects exclusive of thermal aging effects. The UTS and hardness at RT of PNC-FMS irradiated at over 600
C were carried out, and the results were compared with those of aging tests to clarify the irradiation effects exclusive of thermal aging effects. The UTS and hardness at RT of PNC-FMS irradiated at over 600  C tended to be lower than those of as-received and/or thermal aged ones. The facts indicate evident irradiation softening. On the other hand, PNC-FMS irradiated at 835
C tended to be lower than those of as-received and/or thermal aged ones. The facts indicate evident irradiation softening. On the other hand, PNC-FMS irradiated at 835  C was harder than that of aged one. Transformation during irradiation would be the cause.
C was harder than that of aged one. Transformation during irradiation would be the cause.
Tanno, Takashi; Oka, Hiroshi; Yano, Yasuhide; Kurishita, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
Fracture toughness is an important property when ferritic martensitic steel (FMS) is irradiated and thermally aged. The goal of this study is to develop reasonably miniaturized fracture toughness test technique which can be applied for irradiated or sampled from welded small specimen. In this phase, the capability of miniature 3-point bend (3PB) test technique for evaluating toughness, and the side groove effect on miniatured specimen were confirmed. A miniature 3PB type J test conforming to ASTM 1820 was applied to the PNC-FMS developed for the fast reactor. The effect of the root radius of the side groove that controls the crack propagation was verified for the specimen miniaturized to 5 mm thickness, 3 mm width and 22.5 mm length according to the thickness of the wrapper tube. The crack winded and/or branched with root radius of 0.5 mm, the standard size of ASTM1820. But by making it 0.05 mm, it was possible to control the crack propagation along the side groove. As a result, J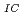 = 300 kJ/m
= 300 kJ/m was obtained, and a prospect of this technique was obtained for the fracture toughness evaluation of the wrapper tube by improving the side groove.
was obtained, and a prospect of this technique was obtained for the fracture toughness evaluation of the wrapper tube by improving the side groove.
Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Oka, Hiroshi*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
Miniature 3 point bend test was applied to evaluate fracture toughness of ferritic/martensitic steel (PNC-FMS) for fast reactor subassembly wrapper tube. In this work, it was clarified that pre-crack length and open angle of side groove are important to obtain the certain and conservative fracture toughness with miniatured specimen. Finally, the fracture toughness value J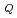 of PNC-FMS could be obtained with miniaturized specimen which can be applied to wrapper tube thickness.
of PNC-FMS could be obtained with miniaturized specimen which can be applied to wrapper tube thickness.